Molecular geometries of covalent molecules lab answers delve into the captivating realm of molecular architecture, where the spatial arrangement of atoms within molecules unveils their properties and behavior. Understanding these geometries is crucial for deciphering the intricacies of chemical reactions, material design, and biological processes.
This exploration begins with an elucidation of molecular geometry and its profound influence on the physical characteristics of covalent molecules. The VSEPR theory emerges as a guiding principle, enabling the prediction of molecular shapes based on electron pair repulsions. The interplay between geometry and properties, such as polarity, boiling point, and melting point, is meticulously examined, showcasing the profound impact of molecular architecture on macroscopic observations.
Molecular Geometry of Covalent Molecules
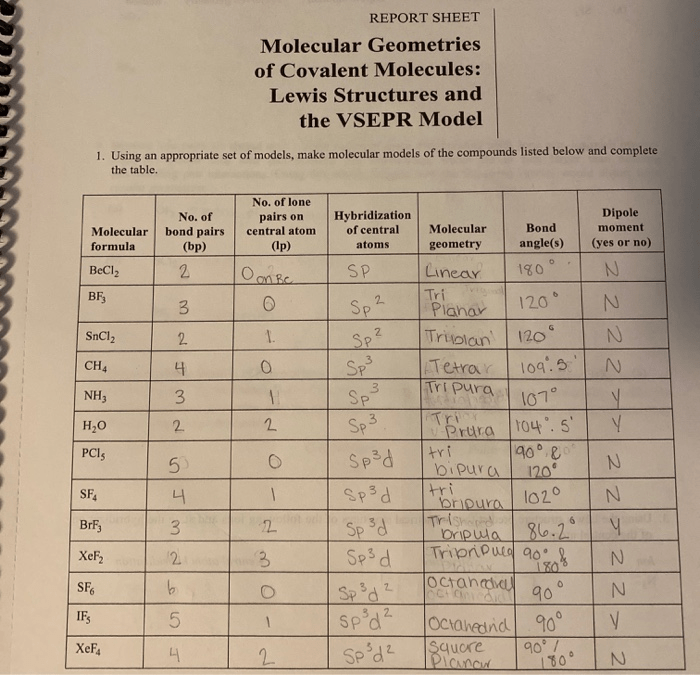
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It is crucial in determining the physical and chemical properties of covalent molecules.
Methods for Determining Molecular Geometry
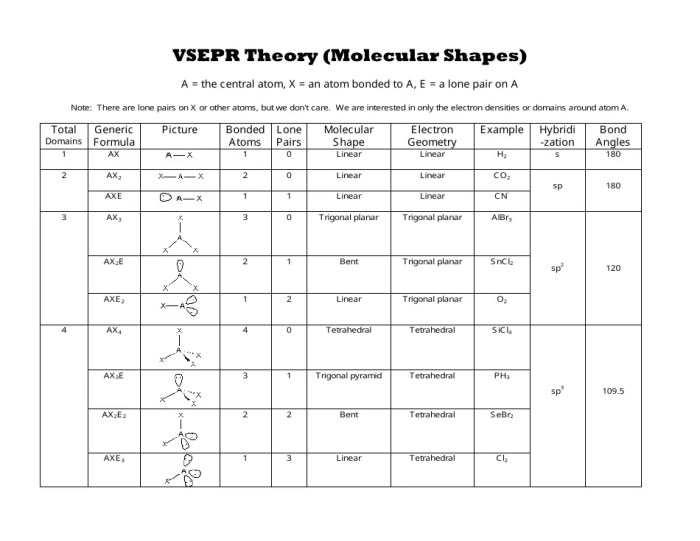
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a widely used method for predicting molecular geometry. It assumes that electron pairs around a central atom repel each other, resulting in a geometry that minimizes this repulsion.
Molecular Geometry and Physical Properties
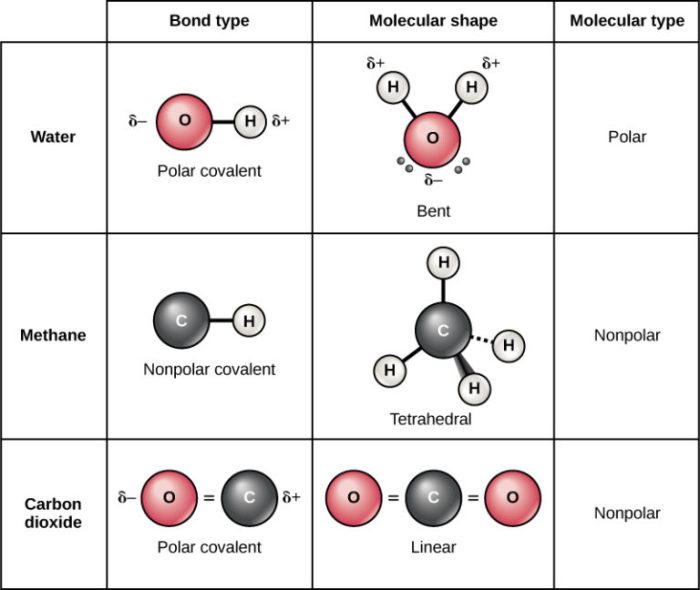
Molecular geometry influences various physical properties, such as:
- Polarity: The uneven distribution of electron density within a molecule.
- Boiling point: The temperature at which a liquid transforms into a gas.
- Melting point: The temperature at which a solid transforms into a liquid.
Applications of Molecular Geometry, Molecular geometries of covalent molecules lab answers
Molecular geometry has numerous applications in various fields:
- Chemistry: Understanding the structure and reactivity of molecules.
- Biology: Predicting the interactions between biomolecules.
- Materials science: Designing materials with specific properties.
FAQ: Molecular Geometries Of Covalent Molecules Lab Answers
What is molecular geometry?
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule.
How does molecular geometry affect physical properties?
Molecular geometry influences properties such as polarity, boiling point, and melting point by determining the distribution of electrons and intermolecular forces.
What is VSEPR theory?
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory predicts molecular geometry based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom.