Embark on a scientific voyage with Amoeba Sisters DNA Replication Answers, a comprehensive guide that deciphers the intricacies of DNA replication. This fundamental process underpins the very essence of life, shaping the genetic heritage of every living organism.
From the structure of DNA to the intricate steps of replication, this exploration unveils the mechanisms that govern the transmission of genetic information, ensuring the continuity and evolution of life on Earth.
Introduction to Amoeba Sisters DNA Replication: Amoeba Sisters Dna Replication Answers
The Amoeba Sisters DNA replication video provides a comprehensive overview of the process by which DNA is duplicated during cell division. DNA replication is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next and plays a crucial role in growth, development, and the maintenance of life.
Key Concepts in DNA Replication

DNA Structure
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a double-stranded molecule that contains the genetic instructions for all living organisms. It consists of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These nucleotides are arranged in a specific sequence that determines the genetic code.
Base Pairing
During DNA replication, the two strands of DNA separate, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. The nucleotides on the new strands pair with the nucleotides on the template strand according to the base pairing rules: A pairs with T, and C pairs with G.
DNA Unwinding and Helicase Enzyme
To initiate DNA replication, the DNA double helix must be unwound. This process is facilitated by the enzyme helicase, which breaks the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs and separates the two strands.
Steps of DNA Replication
Initiation
DNA replication begins at specific locations called origins of replication. At each origin, the enzyme DNA polymerase binds to the DNA and begins to synthesize new strands.
DNA Polymerase
DNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for adding nucleotides to the growing DNA strand. It reads the template strand and adds complementary nucleotides one at a time, following the base pairing rules.
Leading and Lagging Strands
On one strand of DNA, the new strand is synthesized continuously in the 5′ to 3′ direction. This strand is called the leading strand. On the other strand, the new strand is synthesized in short fragments called Okazaki fragments in the 5′ to 3′ direction.
These fragments are later joined together to form the lagging strand.
Regulation of DNA Replication
Control of Initiation
The initiation of DNA replication is tightly regulated to ensure that DNA is replicated only once per cell cycle. This regulation involves proteins that bind to the origin of replication and prevent DNA polymerase from binding until the appropriate conditions are met.
Checkpoints and Repair Mechanisms
DNA replication is a complex process that can be prone to errors. To ensure the accuracy of replication, there are several checkpoints and repair mechanisms in place. These mechanisms can detect and correct errors in the newly synthesized DNA.
Applications of DNA Replication
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
DNA replication is essential for biotechnology and genetic engineering. It allows scientists to manipulate and modify DNA to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) with desired traits.
Medical Diagnostics and Forensics, Amoeba sisters dna replication answers
DNA replication is used in medical diagnostics to identify genetic disorders and in forensics to match DNA samples to individuals.
Comparisons and Contrasts
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
DNA replication differs between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes have a single circular chromosome, while eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes. Additionally, the initiation and regulation of DNA replication are more complex in eukaryotes.
Illustrations and Visualizations
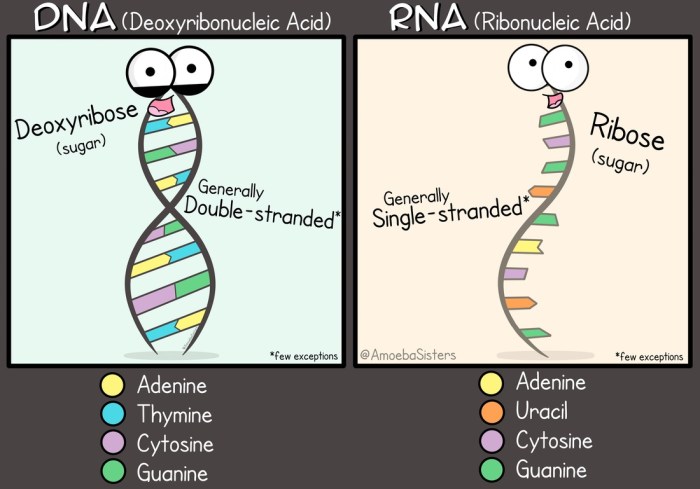
Table: Key Steps of DNA Replication
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Initiation | DNA polymerase binds to the origin of replication. |
| Elongation | DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand. |
| Termination | DNA polymerase reaches the end of the template strand. |
Popular Questions
What is DNA replication?
DNA replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its DNA, creating two identical copies.
Why is DNA replication important?
DNA replication is essential for cell division and the growth and development of organisms.
What are the key steps of DNA replication?
The key steps of DNA replication include unwinding the DNA double helix, synthesizing new DNA strands, and proofreading the newly synthesized DNA.